Indoor location is currently the subject of intensive research. The main goal of researchers is to obtain a functional system capable of locating, identifying and guiding, as precisely as possible and in real time. To date, no solution has been able to achieve a location-navigation system as precise and successful as those developed in analogous research such as outdoor location. The main characteristic of a real time positioning system is to know the precise position of an object or individual within a building, which would make it possible to develop and offer a vast set of services, most notably those that aim to control access through the identification of users, security based on physical location, and applications that pursue a statistical objective or installation management.
The main reason for not having yet achieved this milestone is primarily due to technical issues and, to a greater extent, financial reasons. A GPS system simply requires a physical device that is connected in an open space to a finite number of satellites. On the other hand, a closed space requires the use of an existing infrastructure with a large number of stationary devices that act as beacons, which results in a high cost solution.
Due to the need of improving the accuracy and reducing cost in indoor location system, the research group has developed a hybrid location system with a multi-agent system that uses electromagnetic fields and different types of sensors to track elements such as people or devices.
Specifically, the proposed system has solved the problem to estimating the probabilities of belonging to the points previously scanned in the intensity maps. The intensity maps obtained indoors are created using some parameters. Each of the them contains the information of electromagnetic fields such as: Wi-Fi, GSM, GPRS, RFID, Bluetooth, ZigBee networks scanned in that moment and identified by a coordinate (x,y). The rows can contain more or less columns depending on the scanned intensities.
The deployment of these applications tends to take place in indoor locations such as hospitals, manufacturing plants, large warehouses or even with complementary systems such as GPS (Global Positioning System).
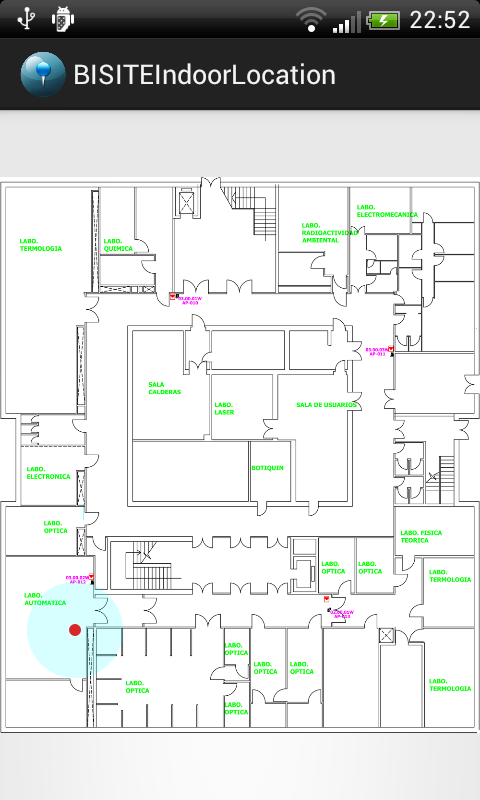
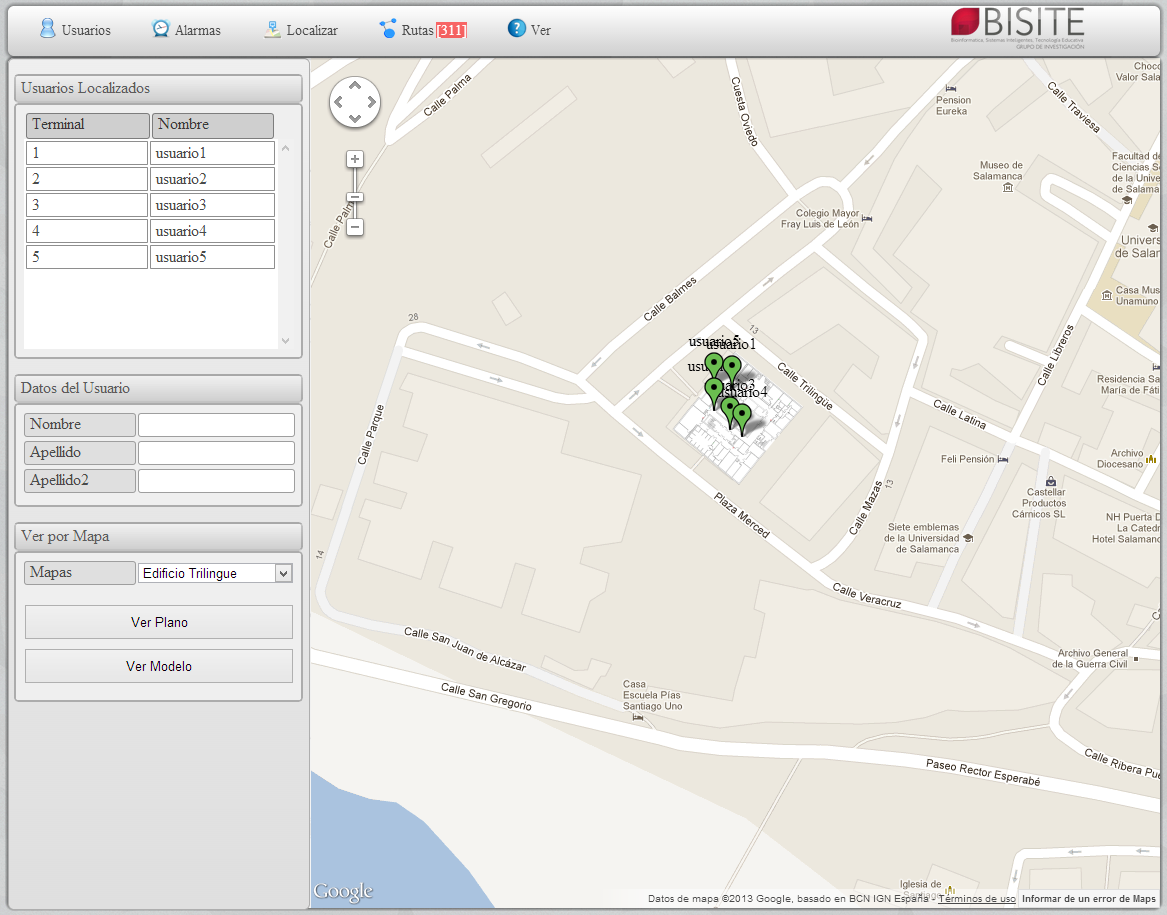
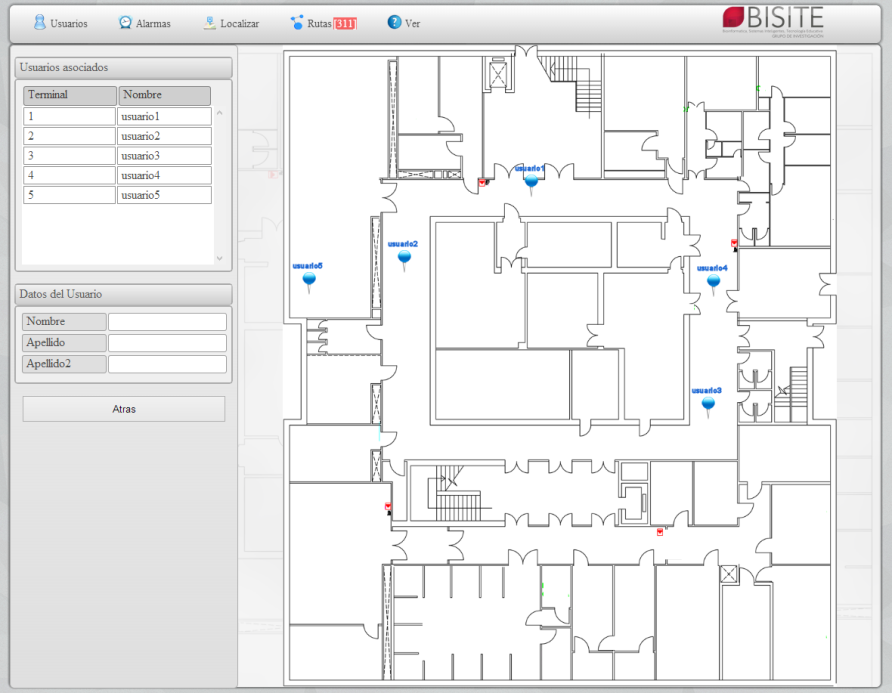
The system may display heat maps, locate in real time users and devices and set different alarms depending on their location. In addition, the system allows detecting anomalous routes by defining graphs using the information of previous routes of users and devices.
Some applications of this technology are:
- Locate staff in hospitals, staff of surveillance and security.
- Locate expensive devices.
- Guidance in shopping malls, monuments and large building.